| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1164930 | 1491052 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
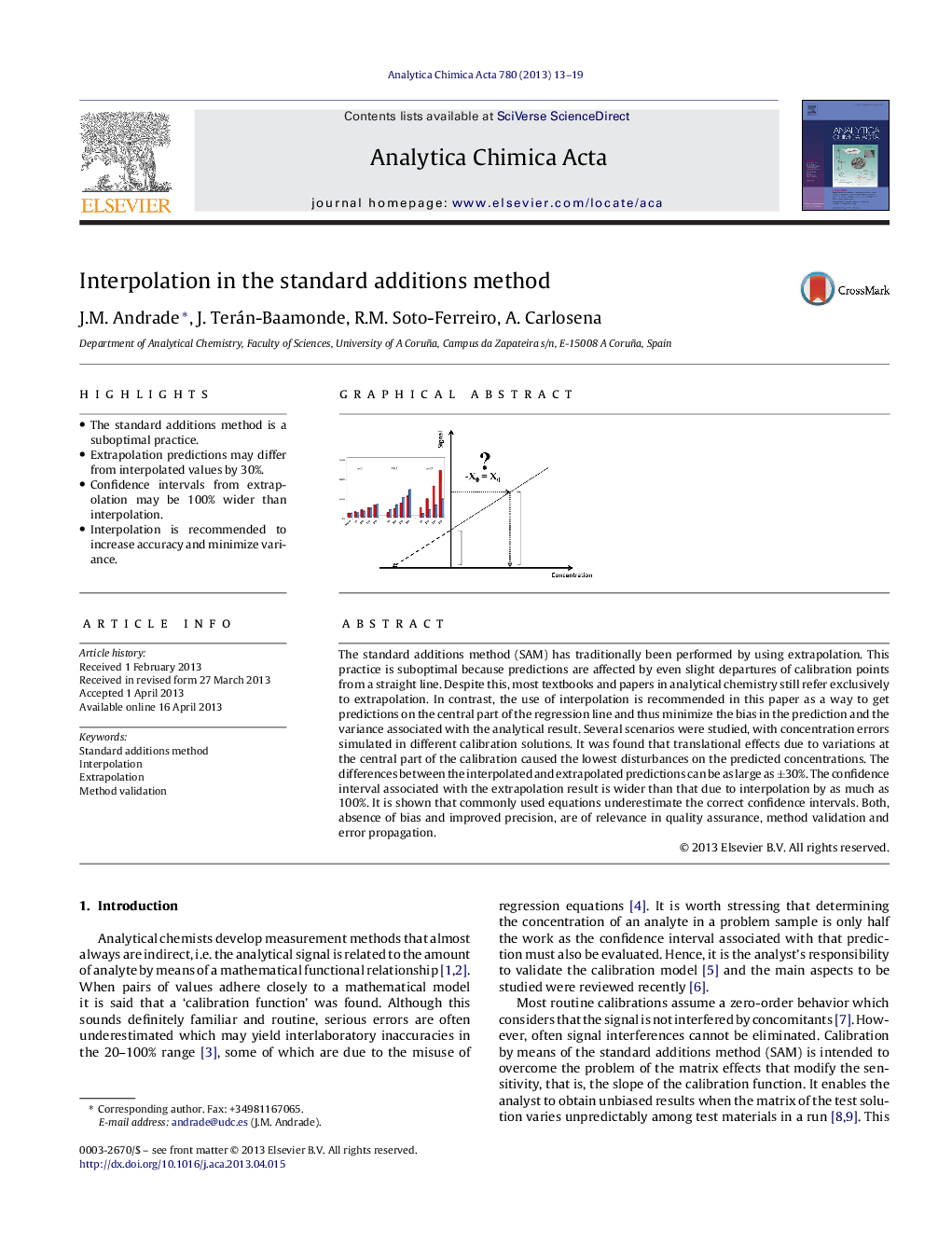
• The standard additions method is a suboptimal practice.
• Extrapolation predictions may differ from interpolated values by 30%.
• Confidence intervals from extrapolation may be 100% wider than interpolation.
• Interpolation is recommended to increase accuracy and minimize variance.
The standard additions method (SAM) has traditionally been performed by using extrapolation. This practice is suboptimal because predictions are affected by even slight departures of calibration points from a straight line. Despite this, most textbooks and papers in analytical chemistry still refer exclusively to extrapolation. In contrast, the use of interpolation is recommended in this paper as a way to get predictions on the central part of the regression line and thus minimize the bias in the prediction and the variance associated with the analytical result. Several scenarios were studied, with concentration errors simulated in different calibration solutions. It was found that translational effects due to variations at the central part of the calibration caused the lowest disturbances on the predicted concentrations. The differences between the interpolated and extrapolated predictions can be as large as ±30%. The confidence interval associated with the extrapolation result is wider than that due to interpolation by as much as 100%. It is shown that commonly used equations underestimate the correct confidence intervals. Both, absence of bias and improved precision, are of relevance in quality assurance, method validation and error propagation.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 780, 30 May 2013, Pages 13–19