| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146025 | 456356 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
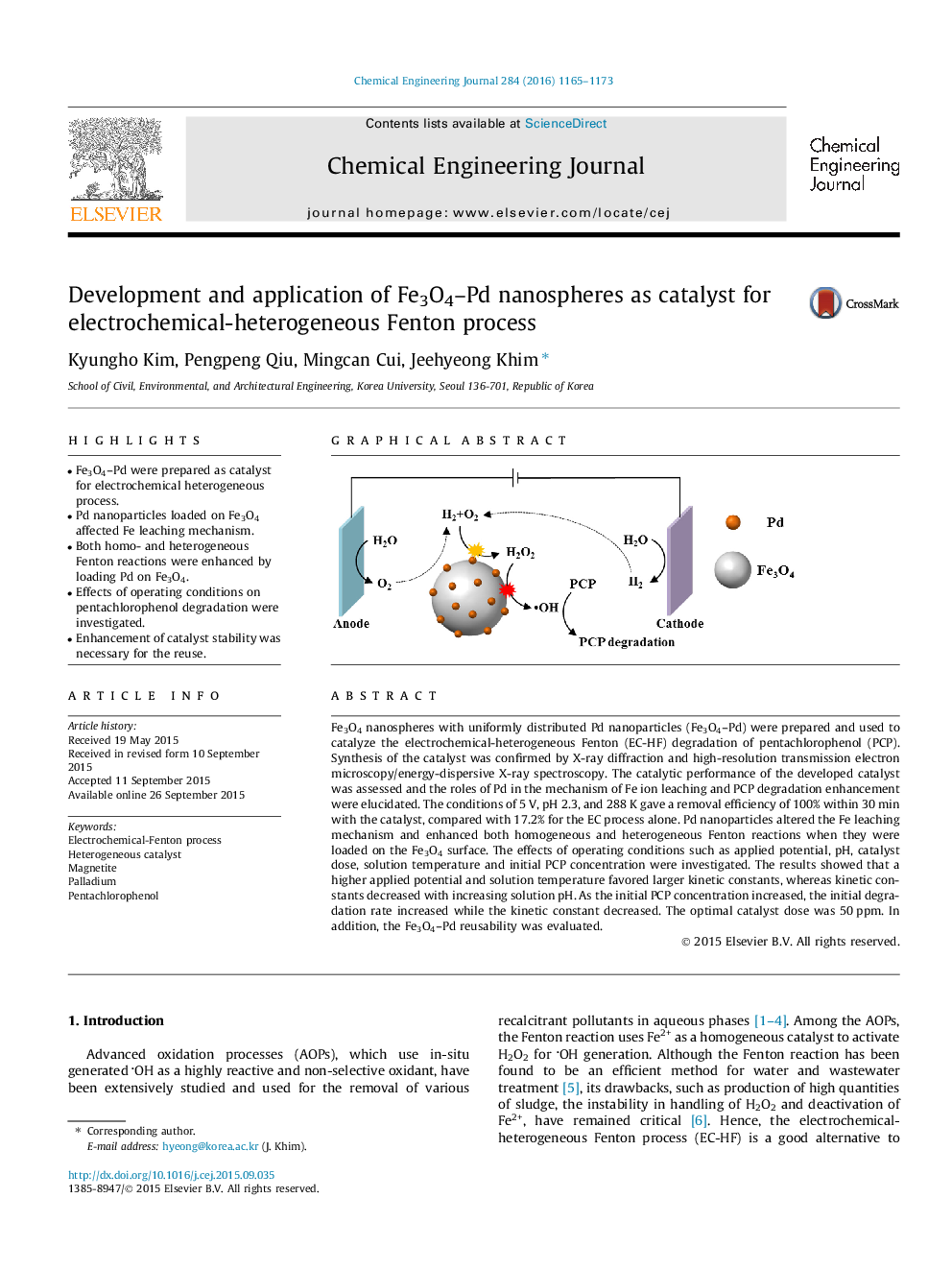
• Fe3O4–Pd were prepared as catalyst for electrochemical heterogeneous process.
• Pd nanoparticles loaded on Fe3O4 affected Fe leaching mechanism.
• Both homo- and heterogeneous Fenton reactions were enhanced by loading Pd on Fe3O4.
• Effects of operating conditions on pentachlorophenol degradation were investigated.
• Enhancement of catalyst stability was necessary for the reuse.
Fe3O4 nanospheres with uniformly distributed Pd nanoparticles (Fe3O4–Pd) were prepared and used to catalyze the electrochemical-heterogeneous Fenton (EC-HF) degradation of pentachlorophenol (PCP). Synthesis of the catalyst was confirmed by X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy/energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The catalytic performance of the developed catalyst was assessed and the roles of Pd in the mechanism of Fe ion leaching and PCP degradation enhancement were elucidated. The conditions of 5 V, pH 2.3, and 288 K gave a removal efficiency of 100% within 30 min with the catalyst, compared with 17.2% for the EC process alone. Pd nanoparticles altered the Fe leaching mechanism and enhanced both homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton reactions when they were loaded on the Fe3O4 surface. The effects of operating conditions such as applied potential, pH, catalyst dose, solution temperature and initial PCP concentration were investigated. The results showed that a higher applied potential and solution temperature favored larger kinetic constants, whereas kinetic constants decreased with increasing solution pH. As the initial PCP concentration increased, the initial degradation rate increased while the kinetic constant decreased. The optimal catalyst dose was 50 ppm. In addition, the Fe3O4–Pd reusability was evaluated.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 284, 15 January 2016, Pages 1165–1173