| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4408142 | 1618832 | 2015 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
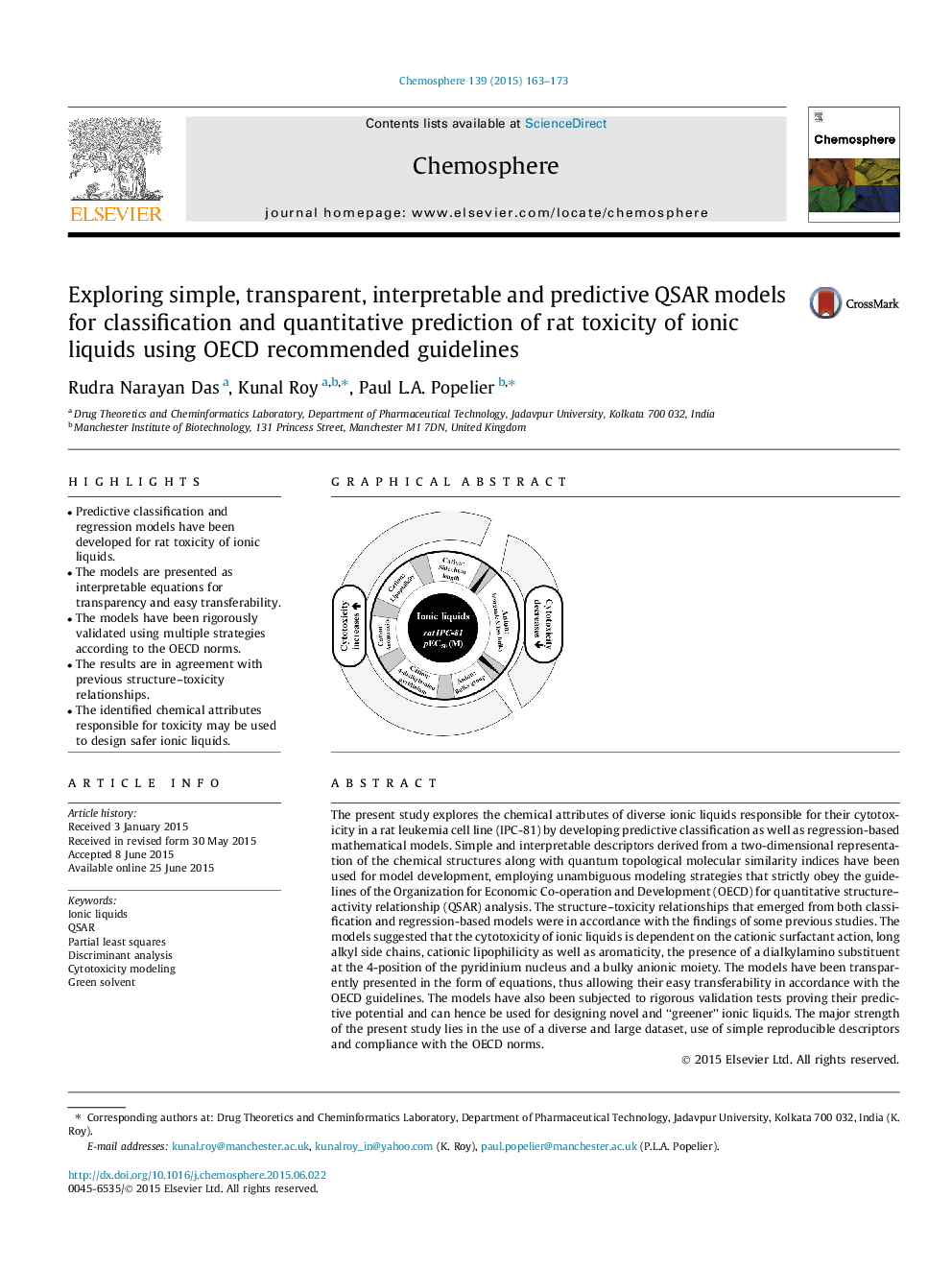
• Predictive classification and regression models have been developed for rat toxicity of ionic liquids.
• The models are presented as interpretable equations for transparency and easy transferability.
• The models have been rigorously validated using multiple strategies according to the OECD norms.
• The results are in agreement with previous structure–toxicity relationships.
• The identified chemical attributes responsible for toxicity may be used to design safer ionic liquids.
The present study explores the chemical attributes of diverse ionic liquids responsible for their cytotoxicity in a rat leukemia cell line (IPC-81) by developing predictive classification as well as regression-based mathematical models. Simple and interpretable descriptors derived from a two-dimensional representation of the chemical structures along with quantum topological molecular similarity indices have been used for model development, employing unambiguous modeling strategies that strictly obey the guidelines of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) for quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) analysis. The structure–toxicity relationships that emerged from both classification and regression-based models were in accordance with the findings of some previous studies. The models suggested that the cytotoxicity of ionic liquids is dependent on the cationic surfactant action, long alkyl side chains, cationic lipophilicity as well as aromaticity, the presence of a dialkylamino substituent at the 4-position of the pyridinium nucleus and a bulky anionic moiety. The models have been transparently presented in the form of equations, thus allowing their easy transferability in accordance with the OECD guidelines. The models have also been subjected to rigorous validation tests proving their predictive potential and can hence be used for designing novel and “greener” ionic liquids. The major strength of the present study lies in the use of a diverse and large dataset, use of simple reproducible descriptors and compliance with the OECD norms.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 139, November 2015, Pages 163–173