| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593723 | 1453952 | 2013 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
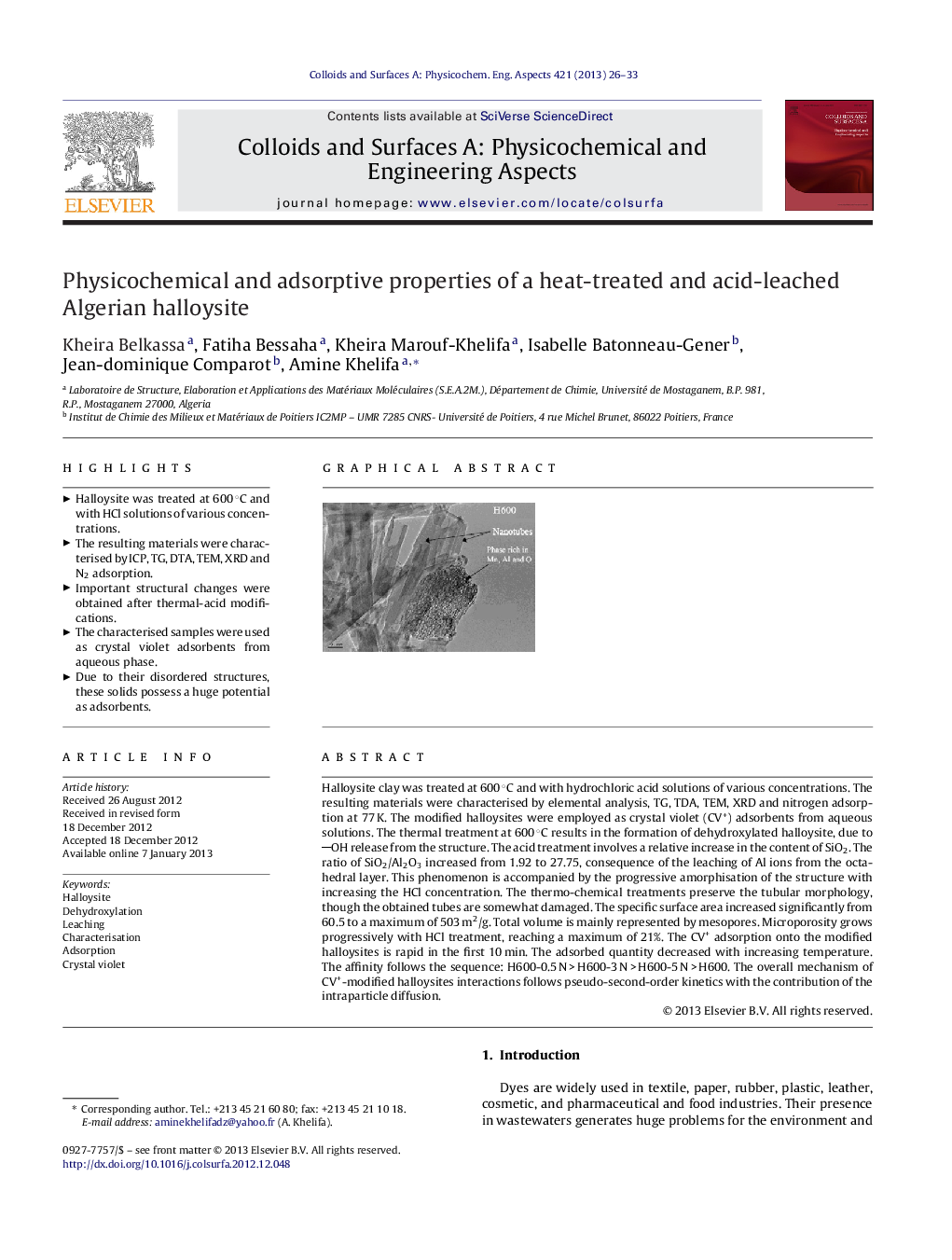
Halloysite clay was treated at 600 °C and with hydrochloric acid solutions of various concentrations. The resulting materials were characterised by elemental analysis, TG, TDA, TEM, XRD and nitrogen adsorption at 77 K. The modified halloysites were employed as crystal violet (CV+) adsorbents from aqueous solutions. The thermal treatment at 600 °C results in the formation of dehydroxylated halloysite, due to OH release from the structure. The acid treatment involves a relative increase in the content of SiO2. The ratio of SiO2/Al2O3 increased from 1.92 to 27.75, consequence of the leaching of Al ions from the octahedral layer. This phenomenon is accompanied by the progressive amorphisation of the structure with increasing the HCl concentration. The thermo-chemical treatments preserve the tubular morphology, though the obtained tubes are somewhat damaged. The specific surface area increased significantly from 60.5 to a maximum of 503 m2/g. Total volume is mainly represented by mesopores. Microporosity grows progressively with HCl treatment, reaching a maximum of 21%. The CV+ adsorption onto the modified halloysites is rapid in the first 10 min. The adsorbed quantity decreased with increasing temperature. The affinity follows the sequence: H600-0.5 N > H600-3 N > H600-5 N > H600. The overall mechanism of CV+-modified halloysites interactions follows pseudo-second-order kinetics with the contribution of the intraparticle diffusion.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Halloysite was treated at 600 °C and with HCl solutions of various concentrations.
► The resulting materials were characterised by ICP, TG, DTA, TEM, XRD and N2 adsorption.
► Important structural changes were obtained after thermal-acid modifications.
► The characterised samples were used as crystal violet adsorbents from aqueous phase.
► Due to their disordered structures, these solids possess a huge potential as adsorbents.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 421, 20 March 2013, Pages 26–33