| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465803 | 1422957 | 2017 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
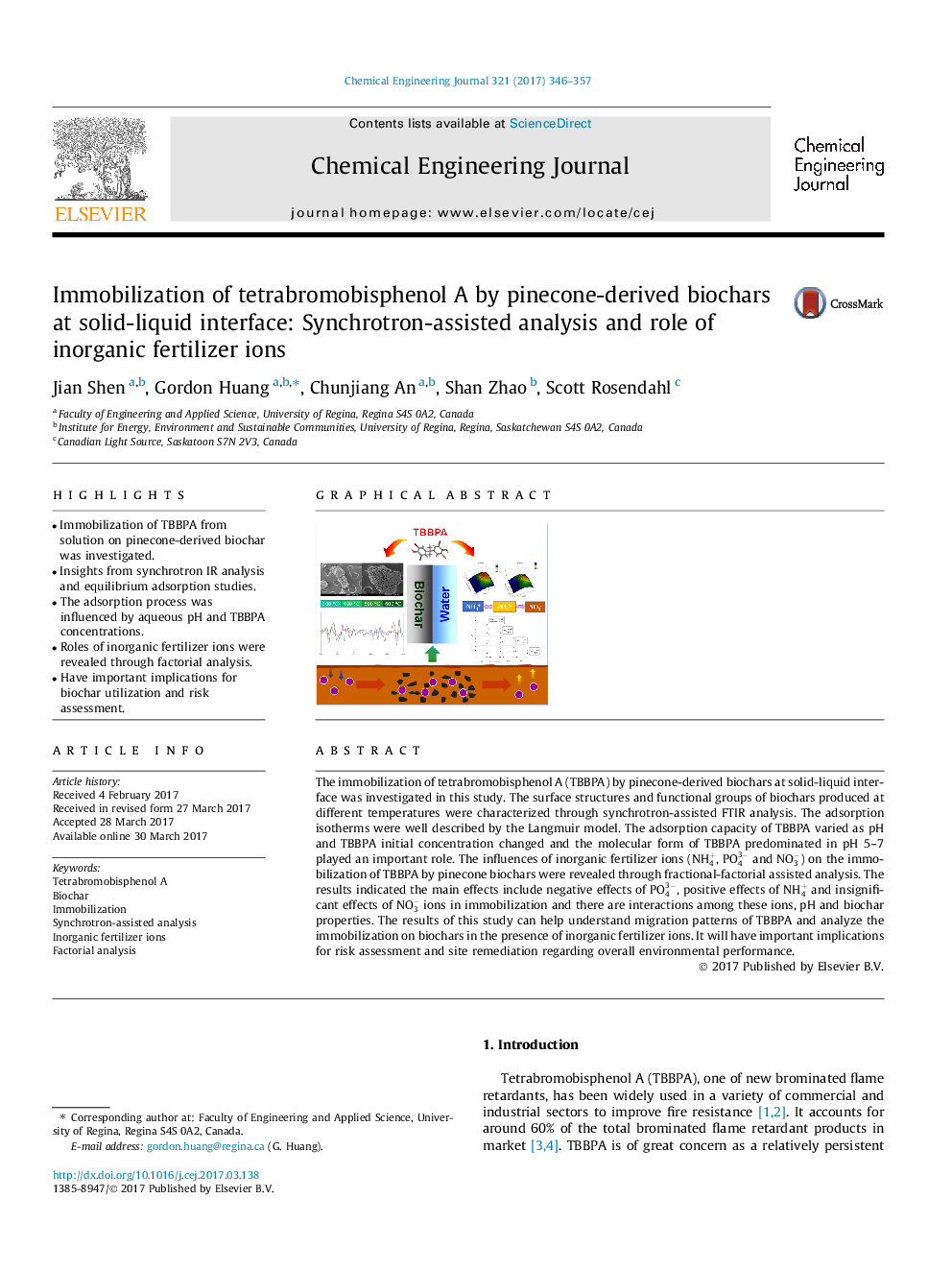
- Immobilization of TBBPA from solution on pinecone-derived biochar was investigated.
- Insights from synchrotron IR analysis and equilibrium adsorption studies.
- The adsorption process was influenced by aqueous pH and TBBPA concentrations.
- Roles of inorganic fertilizer ions were revealed through factorial analysis.
- Have important implications for biochar utilization and risk assessment.
The immobilization of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) by pinecone-derived biochars at solid-liquid interface was investigated in this study. The surface structures and functional groups of biochars produced at different temperatures were characterized through synchrotron-assisted FTIR analysis. The adsorption isotherms were well described by the Langmuir model. The adsorption capacity of TBBPA varied as pH and TBBPA initial concentration changed and the molecular form of TBBPA predominated in pH 5-7 played an important role. The influences of inorganic fertilizer ions (NH4+, PO43- and NO3-) on the immobilization of TBBPA by pinecone biochars were revealed through fractional-factorial assisted analysis. The results indicated the main effects include negative effects of PO43-, positive effects of NH4+ and insignificant effects of NO3- ions in immobilization and there are interactions among these ions, pH and biochar properties. The results of this study can help understand migration patterns of TBBPA and analyze the immobilization on biochars in the presence of inorganic fertilizer ions. It will have important implications for risk assessment and site remediation regarding overall environmental performance.
151
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 321, 1 August 2017, Pages 346-357