| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 74160 | 49082 | 2012 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
Diffusion of methane in two different samples of DDR crystals (one of which had been subjected to a proprietary treatment) has been studied experimentally by the ZLC technique. Measurements were made over a wide range of temperatures (273–423 K) and purge flow rates. The ZLC response curves for both samples are shown to be consistent with the simple model of intra-crystalline diffusion control with no evidence of any significant surface resistance. The derived equilibrium constants and diffusivities are consistent with the limited published data already available for this system. There is a significant difference in both diffusivity and diffusional activation energy between the untreated and treated samples suggesting a somewhat larger free aperture for the windows of the treated sample. For both samples the diffusivity of methane is substantially increased in the presence of a CO2 atmosphere; as is to be expected from transition state theory for a competitive adsorption system.
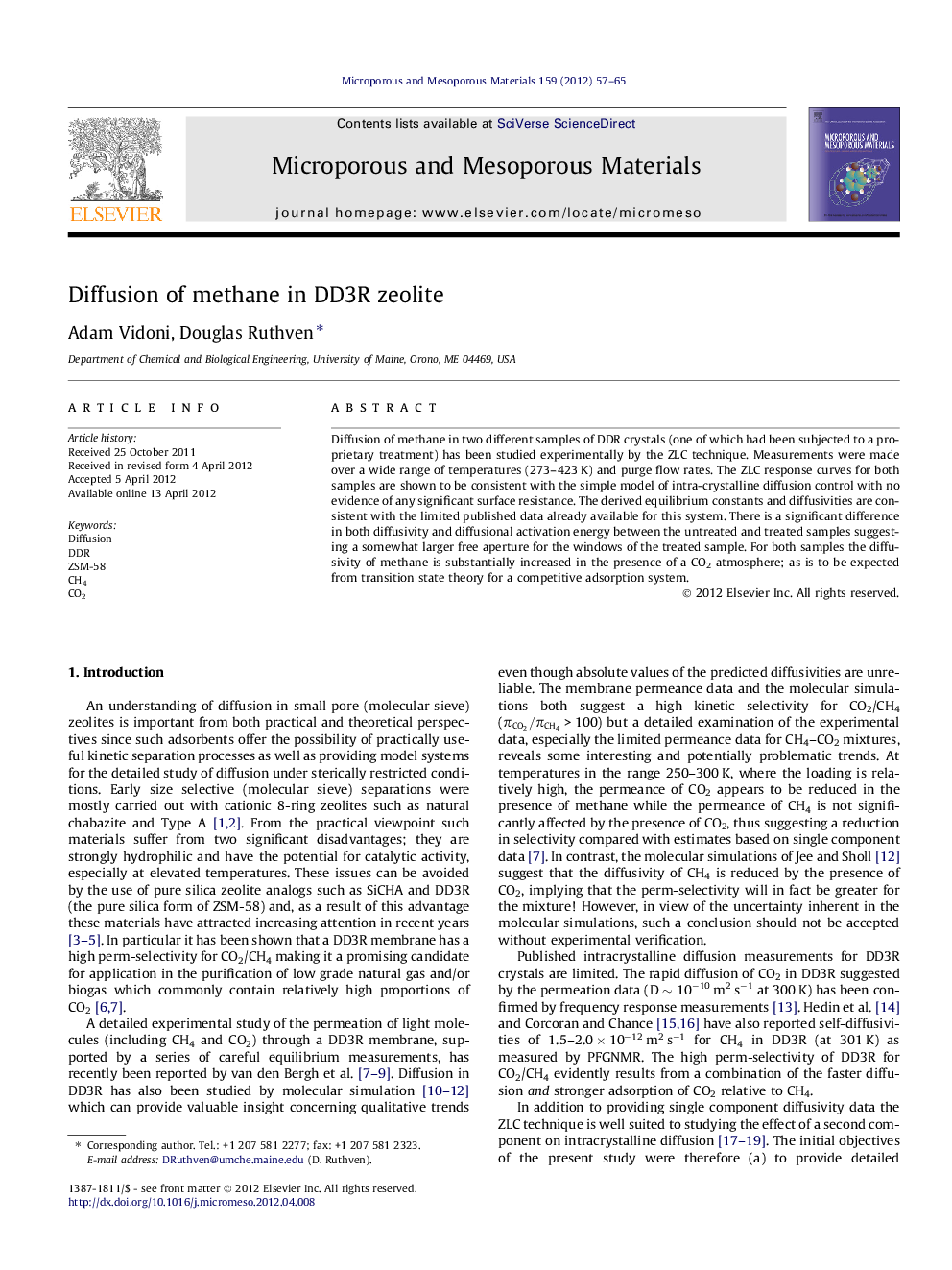
Unit cell of DDR and 19-Hedral Cavity accessed by three distorted 8-Rings (From Atlas of Zeolite Structures).Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Diffusivities and activation energies have been measured for methane in DDR.
► The diffusivity of methane in DDR is enhanced by CO2.
► Consistent with transition state theory but contradicts recent molecular simulations.
Journal: Microporous and Mesoporous Materials - Volume 159, 1 September 2012, Pages 57–65